The UN Environmental Program (UNEP)’s latest two Adaptation Gap Reports have emphasized the importance of nature-based solutions (NBS) to mitigate climate change. So what are nature-based solutions, and why should adaptation efforts focus on them?
UNEP Adaptation Gap Reports
In the 2021 Adaptation Gap Report, UNEP warns that the extreme events experienced throughout the year prove that climate outcomes are likely to be worse than optimistic estimates, and therefore that adaptation efforts should be more ambitious than they currently are. “More than anything else, these events underscore the urgent need to decarbonize the global economy much faster than [nationally determined contributions] NDCs currently foresee. This is the only way to avoid escalating climate risks and to prevent the adaptation gap from widening further,” the authors say.
This is not the first time we hear about the need to act more drastically against climate change. But what’s interesting about the UNEP report is the analysis of what type of solution deserves the most focus: nature-based solutions. According to the Global Commission on Adaptation, investment in climate adaptation delivers benefit–cost ratios of between 2:1 and 10:1, largely through avoiding future costs. UNEP identifies nature-based solutions as “a source of investment with the potential to reduce climate risks and vulnerability, while providing economic, environmental, and social inclusion co-benefits”. In fact, it is estimated that for every dollar spent on ecosystem conservation (a form of nature-based solution), almost seven more are generated in the economy over five years.
What are nature-based solutions?
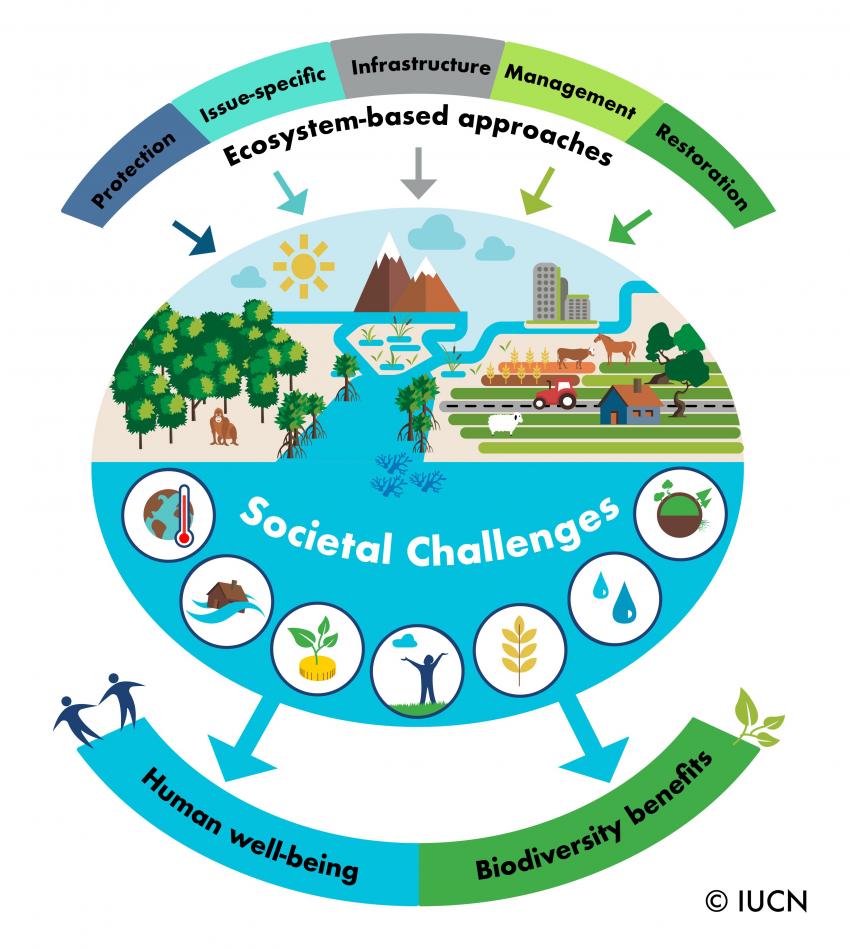
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) defines nature-based solutions as “actions to protect, sustainably manage, and restore natural or modified ecosystems, that address societal challenges effectively and adaptively, simultaneously providing human well-being and biodiversity benefits”. They can be categorized into five types: avoided deforestation, peatland impact, peatland restoration, reforestation, and cover crops. In a nutshell, nature-based solutions promote the resilience of natural ecosystems.
IUCN has developed eight principles to characterize nature-based solutions: they must embrace nature conservation norms and principles; they can be implemented alone or in an integrated manner with other solutions to societal challenges, such as technological and engineering solutions; they are determined by site-specific natural and cultural contexts that include traditional, local and scientific knowledge; they produce societal benefits in a fair and equitable way, in a manner that promotes transparency and broad participation; they maintain biological and cultural diversity and the ability of ecosystems to evolve over time; they are applied at a landscape scale; they recognise and address the trade-offs between the production of a few immediate economic benefits for development, and future options for the production of the full range of ecosystems services; and they are an integral part of the overall design of policies, and measures or actions, to address a specific challenge.
The potential of nature-based solutions to fight climate change
According to the UN Global Compact, nature-based solutions can mitigate 10-12 gigatons of CO2 per year – over one-third of the cost-effective climate mitigation needed between now and 2030 to limit global warming to below 2°C.
What makes nature-based solutions so appealing in the fight against climate change is that they tend to be cheaper than technological solutions such as solar panels or wind turbines, and at the same time each project tends to cover several sustainable development goals (SDGs). “Nature-Based Solutions underpin the Sustainable Development Goals: they support vital ecosystem services, biodiversity, and access to fresh water, improved livelihoods, healthy diets and food security from sustainable food systems,” says the UN Global Compact. This means their positive impact on the climate is deep and durable.
For these reasons, nature-based solutions are fast becoming the preferred type of carbon offset for companies looking to become carbon-neutral.
NBS projects on ClimateTrade
Since the beginning of our journey, we have been adding mitigation projects and carbon credits based on the conservation of ecosystems to our marketplace.
The ClimateTrade marketplace currently features 11 NBS projects of this type, including the hemp carbon removal project pilot in Spain, a collaboration between ClimateTrade and Made in Hemp.
In addition, our decentralized platform removes the barriers that prevent reaching the potential of NBS, such as the lack of consensus on how to treat the ownership of sequestered carbon, lack of clarity on rules and certifications for such projects, and lack of confidence after years of excess supply of carbon credits but at very low prices that did not help communities to survive.
On the ClimateTrade marketplace, project developers manage the sale and set the price of their carbon credits. Because they are connected directly to companies looking to offset their carbon footprint, without traditional intermediaries such as brokers, they maintain control over the whole process. At the same time, blockchain traceability ensures that carbon offsetting funds generate real benefits for nature-based projects.