Although challenges remain, the new EU Nature Restoration Law champions biodiversity, climate goals, and offers exciting opportunities through instruments such as voluntary biodiversity credit markets.
In a significant milestone for environmental legislation, the European Union’s Environmental Council has officially adopted the Nature Restoration Law (NRL). This landmark decision follows a challenging legislative journey and represents a major victory for nature conservation, climate action, and the EU Green Deal.
What is the EU Nature Restoration Law?
The EU Nature Restoration Law is aimed at restoring degraded ecosystems across Europe.
But its adoption did not come easily. After surviving a vigorous disinformation campaign aimed at derailing it in the European Parliament, the law faced the risk of rejection in the final discussions. However, a majority of 20 countries, representing 66.07% of the EU population, endorsed the law. Austria’s Environment Minister, Leonore Gewessler, played a crucial role in this outcome by changing her country’s stance at the last minute, ensuring the law’s passage.
What are the nature restoration targets for the EU?
The EU Nature Restoration Law sets ambitious targets for restoring degraded ecosystems across Europe. By 2030, member states are required to restore at least 20% of their land and sea areas, with further milestones extending to 2040 and 2050. The law covers a broad range of ecosystems, including coastal, freshwater, forest, agricultural, urban, wetlands, grasslands, rivers, and lakes. Specific targets include reversing the decline of pollinator populations and planting three billion additional trees by 2030.
Member states must submit national restoration plans to the European Commission, which will review their application by 2033. This ensures accountability and progress toward the law’s goals, reinforcing the EU’s commitment to biodiversity and climate action.

How has public and scientific support influenced the adoption of the EU Nature Restoration Law?
The EU Nature Restoration Law’s journey to adoption was bolstered by massive public and scientific support. Over one million citizens signed petitions and sent messages in favour of the law. Additionally, over 6000 scientists, more than 100 businesses, youth organisations, and various civil society groups advocated for its passage, demonstrating widespread backing across numerous sectors.
What are the challenges faced in restoring ecosystems?
Despite its adoption, the NRL raises several critical questions regarding funding, fairness, and social impact. Ensuring a just transition is paramount to avoid exacerbating urban-rural divides and to support local communities, particularly farmers and landowners, who may face significant changes. Potential solutions include leveraging the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) budget, introducing biodiversity credits, and exploring voluntary biodiversity markets.
What is the Nature Restoration Law and the Green Deal?
The Nature Restoration Law is a cornerstone of the European Green Deal, a comprehensive strategy to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050. Key goals of the Green Deal include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030, promoting renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, developing a circular economy, and protecting biodiversity.

How will the EU Nature Restoration Law affect the UK?
The law’s adoption positions the EU as a leader in global climate and biodiversity efforts. It sets a positive precedent ahead of the UN Biodiversity Conference (CBD COP16), reinforcing Europe’s commitment to its global responsibilities.
For the UK, which is no longer part of the EU, the Nature Restoration Law presents both challenges and opportunities. The UK can choose to either align with the EU’s ambitious environmental standards, pursue its own high-ambition policies, or maintain a less ambitious stance. Regardless of the approach, the EU’s legislation will influence the UK’s markets, trade negotiations, and global climate standing. With elections taking place in the UK currently, we have seen climate policies play a central part in discussions between opposing sides, time will tell on who and what priorities are made in terms of climate and nature responsibilities.
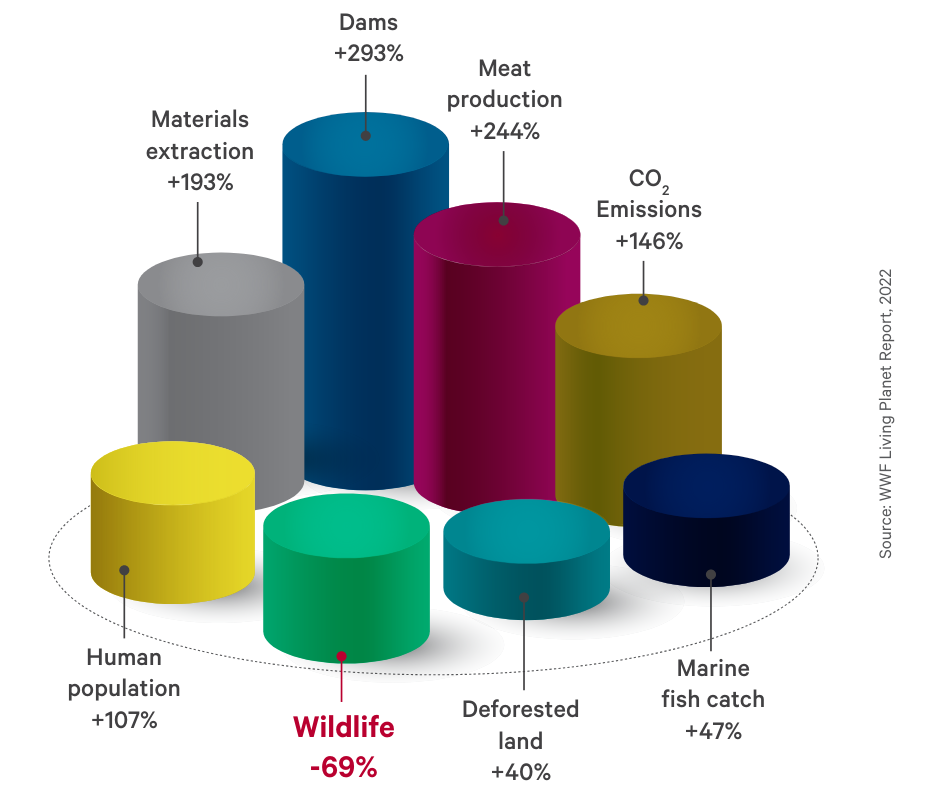
How the world has changed in the last 50 years
What is the business case for biodiversity?
The business case for biodiversity conservation is compelling across various sectors and regions. As highlighted by the European Commission, over half of global GDP relies on nature and its services, crucially supporting industries like construction, agriculture, food production, and healthcare.
Moreover, more than 75% of global food crops depend on pollinators, emphasising the critical role biodiversity plays in food security. However, our current global food systems contribute significantly to environmental degradation, with agriculture alone responsible for 80% of deforestation and 70% of freshwater use, driving terrestrial biodiversity loss. Addressing these challenges is not only essential for environmental sustainability but also for economic resilience.
The EU’s recent adoption of the Nature Restoration Law underscores this perspective, framing nature recovery as an investment in a more productive future aligned with climate and biodiversity goals. Studies indicate that every €1 invested in restoration efforts yields a substantial return of at least €8 in environmental and economic benefits, highlighting the strategic value of biodiversity conservation for long-term prosperity.
The Voluntary Biodiversity Credit Market
ClimateTrade has been at the forefront of championing biodiversity, a pioneering advocate and seller of biodiversity credits. Alongside Terrasos, ClimateTrade was one of the earliest organisations to introduce and promote these innovative financial instruments, which are designed to support conservation efforts by assigning economic value to biodiversity preservation. Our initiatives have gained significant recognition and support, including endorsement from the World Economic Forum. By facilitating investments in biodiversity credits, we have enabled businesses and individuals to contribute to the restoration and protection of natural ecosystems, thus playing a crucial role in global sustainability efforts.
Javier Santoyo, Commercial Development Director at ClimateTrade said –
“The EU Council has approved the Nature Restoration Law (NRL) with a qualified majority of 66%, marking a significant victory for the European Union and its citizens and finally, we have clear goals for nature restoration.
An exciting opportunity lies in the development of voluntary biodiversity credit’s markets. These markets allow businesses and individuals to invest in biodiversity conservation by purchasing credits that fund restoration projects. Along with Terrasos, early pioneers in this field, we have shown how biodiversity credits can attract investment and support large-scale ecological restoration. Endorsed by the World Economic Forum, these markets offer a promising avenue to finance the ambitious goals set by the NRL, providing economic incentives for companies to contribute positively to the environment.
While there are many questions to address, today is a great day for everyone committed to a greener future. The EU Green Deal is thriving, with the goal to restore at least 20% of EU land and sea by 2030 and all ecosystems in need by 2050.”
With the restoration of these diverse ecosystems across Europe, there will be significant potential for the development of biodiversity credits. This initiative is expected to garner increased awareness and engagement from companies eager to invest in conservation efforts. The restoration targets set by the EU Nature Restoration Law create an optimal environment for the growth of biodiversity credit markets, enhancing their reputation and scalability. This approach not only incentivizes businesses to contribute to ecological restoration but also aligns with global sustainability goals, marking a pivotal step towards a more resilient and biodiverse future.
If you want to learn how to integrate biodiversity into your business strategy, contact the ClimateTrade team today and take a step towards a greener future.








